- "Boucle Centre-Artibonite" d'Haïti FR ES
- Antigua-et-Barbuda FR
- Bahamas FR
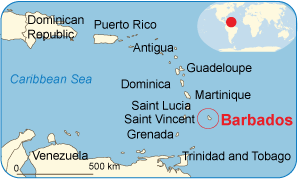
- Barbados
- Haïti FR
- Haïti : De ruptures en ruptures, un territoire en mutation FR ES
- Haïti : La persistance d'un état de crise et de la crise de l'Etat FR ES
- Haïti : Situation de l'agriculture 2024 FR
- Haïti : les empreintes majeures d'une identité plurielle FR ES
- Jamaïque FR
- La Guyane : un des derniers Far West FR
- La Martinique : un mal développement îlien FR ES
- Martinique
- Port of Fort-de-France (Martinique)
- Port of Pointe-à-Pitre/Jarry (Guadeloupe)
- Puerto Rico
- République dominicaine FR ES
- St. Vincent and the Grenadines
- Trinidad and Tobago (2000-2005)
- Venezuela FR
|
Barbados
Indépendence: 30.11.1966
|
The flag adopted on 30th November 1966 comprises three vertical yellow and blue bands symbolising the sea, the sand and the sky. The trident in the centre recalls greek mythology, the trident of Poseidon, marking the direct route between two worlds. |
|||||||||
|
General information
Area: An island of 431 sq. kms
Location: 13°N 59°W Highest landmark: Mount Hillaby (336 m)
Capital: Bridgetown, the only seaport (a major part of the island is surrounded by coral reef).
Population (2011): 273 900 hab. (UNDP) Official language: english Everyday languages: english, bajan (barbadian creole). Currency: barbadian dollar (BBD) with a fixed exchange rate of 1 US$ = 2 BB$ since 1967, that is 1 € = 2.79 BB$ (October 2010).
Independence Day : 30th November |
Political regime
Constitution: Parliamentary monarchy
► Queen: Elisabeth II Bipartisan government:
Governing Party: Democratic Labour Party (DLP) International and regional organisations:
► Member of the UN (09.12.1966) |
Brief History With its Amerindian population, the island was the first European berthing point in the Caribbean. Discovered by the Portuguese in 1536, colony of the United Kingdom from 1627 to its independence in 1966, Barbados became a crossroads between western Europe, the Caribbean islands and some regions of the South American continent. Nicknamed 'Little England' by its neighbours, Barbados remains heavily marked by British influence in spite of the growth of regionalist feelings and cultural nationalism since independence.
|
||||||||
|
Demographic data
Life expectancy (2011): 76.8 years (UNDP) Literacy rate (2008): 99.7%
Poverty (2008): 13% below the poverty threshold Density (2011): 635.5 inhab./km2 Level of urbanisation (2006): 53.69% Religion: Protestant 67% (of which 40% Anglican, 8% Penticostal, 7% Methodist), Catholic 4%, others 12%, atheist 17%.
There are also some small juewish and muslin communities.
Population:
HDI : (UNDP, 2011)
|
Economic data
GDP (2009) : 3 895 million US$ (IMF)
GDP per capita (2009) : 14 116 US$ (IMF) Rate of growth (2009) : - 5.5% Active population (2008) : agriculture 3.3%, industry 17.3%, services 79.4%. Unemployment rate (2010) : 10.4% Rate of inflation (2009) : 2.4% Public deficit (2010) : 97% of GDP Main export clients (2009): Trinidad & Tobago 16.1%, Jamaica 14.4%, Brazil 10.2%, United States 8.1%, Saint Lucia 7.5%. Main import suppliers : Trinidad & Tobago 31.6%, United States 30.7%, Colombia 7.9%, China 5.2 %, United Kingdom 4.8%.
Some strong points: Économy dominated by light industry and toursim sectors. Offshore finance and services are also importants.
Direct flows of investment estimated by UNCTAD at 290 million US$ in 2009, principally in the tourism and construction sectors. |
Cultural particularities
National dish: 'coucou' (base of okra and maïze meal) Personalities:
► Ryan Brathwaite: world champion 2009, 110 m hurdles |
||||||||
|
Recent events
► Cricket world cup 2007: 1 of 8 caribbean island locations.
|
top
|
  |